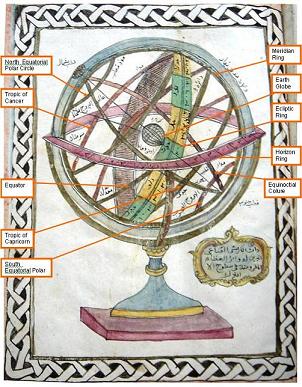
The Armillary Sphere: A Concentrate of Knowledge in Islamic Astronomy
by Samia Khan Published on: 1st December 2007
The armillary sphere is an ancient astronomical instrument reproducing a model of the celestial sphere. In its simplest form, it was known since the antiquity. The article presents the principle of its drawing and use,…

Star-finders Astrolabes
by Cem Nizamoglu Published on: 7th September 2017
Over a thousand-year period in Muslim Civilisation, epoch-making discoveries and contributions, such as the first record of a star system outside our own galaxy were made. Also astronomical instruments including celestial globes, armillary spheres, sextants…

Learning Institutions in Islam
by The Editorial Team Published on: 11th January 2007
Learning institutions in various forms have existed for centuries in the Muslim World, the earliest of which are, al-Qarawiyyin, al-Azhar and al-Qayrawan. This short article traces the emergence and spread of madrasas as a popular…

Modelling the Stars
by Jonathan Chang Published on: 30th June 2004
The measurement of the positions of the stars was developed and refined by scientists of the Muslim world and many kinds of Models were developed. These are described within this article.

Transmission of Muslim Astronomy to Europe
by Salah Zaimeche Published on: 26th December 2001
It was in Muslim Toledo, Spain, where flocked in the 12th century, in particular, scholars from all Christian lands to translate Muslim science, and start the scientific awakening of Europe.

Portable Cosmologies
by Alexandria Hejazi Tsagaris Published on: 8th July 2020
15-16th Century Italian-Islamic Exchanges of the Astrolabe and Effects on Visual Culture

The Observation Well
by Aydin Sayili Published on: 7th June 2008
Observation wells received much historical interest relating to observatories. In this article Prof. Aydin Sayili describes the history of "observation wells" both in Islamic and European worlds.

The Instruments of Istanbul Observatory
by Sevim Tekeli Published on: 8th June 2008
In this article, Professor Sevim Tekeli, an outstanding scholar in the history of Ottoman science, describes the instruments built by Taqî al-Dîn Ibn Ma'ruf and his team at the Istanbul observatory (was in activity between…

Scientific Contacts and Influences Between the Islamic World and Europe: The Case of Astronomy
by Paul Kunitzsch Published on: 25th January 2007
For more than a thousand years the Muslim East and the Christian West, notwithstanding the differences in matters of creed, ideology and social traditions and the intervening opposition of defenders of orthodoxy on both sides,…

The Horizon of Katip Celebi’s Thought
by Bekir Karliga Published on: 16th June 2009
The article of Professor Dr. Bekir Karliga on the horizon of Katip Çelebi's thought is a tremendous analysis of the reformist efforts deployed by the renowned 17th-century Ottoman scholar Katip Çelebi Mustafa bin Abdallah, known…

Oxford Museum of the History of Science Online Al-Mizan Exhibition
by Sairah Yassir-Deane Published on: 16th November 2017
The Oxford Museum of the History of Science launched an online Al-Mizan Exhibition, this exhibition explores the connections between the sciences and arts in societies from Muslim Civilisation.

The Transfer of Science Between India, Europe and China via Muslim Heritage
by Charles Burnett Published on: 15th July 2010
[Proceedings of the conference 1001 Inventions: Muslim Heritage in Our World organised by FSTC, London, 25-26 May 2010]. The Islamic realms served as a crucible for scientific learning from the ancient Greek world in the…

Ali Al-Qushji and His Contributions to Mathematics and Astronomy
by Ilay Ileri Published on: 12th August 2011
Ali Al-Qushji was one of the most noteworthy and important scientists in the Islamic world. He wrote valuable works especially on astronomy and mathematics. He was a student and co-worker of the famous statesman and…

Islamic Astronomy from “Star Wars” to Star Tables
by Glen M. Cooper Published on: 10th November 2017
The most obvious difference between modern and Islamic astronomy is that the latter is primarily mathematical and predictive, and the former has other observational goals, such as describing the physics of other worlds.

Science in Western Islam: Astronomy
by Monica Rius Pinies Published on: 22nd December 2022
The history of science is a fundamental element in constructing a full understanding of the history of society. Furthermore, we must keep in mind that the globalization of ideas has occurred since ancient times, such…

Taqi al-Din Ibn Ma’ruf: A Bio-Bibliographical Essay
by Salim Ayduz Published on: 26th June 2008
This article is a bio-bibliographical essay on the life and works of Taqī al-Dīn Ibn Ma'ruf, a scholar of 16th-century Istanbul, one of the most prolific and original scientists of the Ottoman period of Islamic…

Ibn Yunus and The Pendulum: A History of Errors
by David A King Published on: 29th April 2015
In this article, Professor David A. King explores the authenticity of the statement that tenth-century Egyptian astronomer Ibn Yūnus was the first person to use a pendulum to measure time. After examining evidence originating from…

The Mechanical Water Clock Of Ibn Al-Haytham
by Salim Al-Hassani Published on: 22nd November 2013
The Foundation for Science, Technology and Civilisation (FSTC) announces their new achievement in the history of Islamic clocks. For the first time, the work of Ibn al-Haytham on the water clock (Maqala fi ‘amal al-binkam)…

Abu Ishaq Ibrahim Ibn Yahya Al-Zarqali
by FSTC Published on: 18th July 2007
Al-Zarqali is an eminent Andalusian astronomer of the 11th century who was the foremost astronomer of his time. He excelled in different domains of theoretical and practical astronomy and left works that influenced greatly his…

Biruni’s Telescopic-Shape Instrument for Observing the Lunar Crescent
by S. Mohammad Mozaffari, Georg Zotti Published on: 17th October 2020
This paper deals with an optical aid named barbakh that Abū al-Rayḥān al-Bīrūnī (973–1048 CE) proposes for facilitating the observation of the lunar crescent in his al-Qānūn al-Mas‘ūdī VIII.14. The device consists of a long…






















